10 KiB
Evaluating Text-to-Image Models
The rapid advancement of generative models in fields like text-to-image generation has introduced a plethora of models to the community. Objectively evaluating the performance of these diverse models has become crucial for technology selection and optimization. Traditional evaluation methods heavily rely on manual annotation and subjective judgment, often requiring significant human resources for sample selection, quality scoring, and result analysis. This process is not only time-consuming and costly but also prone to bias due to reviewers' subjective preferences, which is particularly problematic in image generation. For instance, in text-image alignment evaluation, manual scoring involves organizing teams to score thousands of generated images individually, taking days and risking consistency. Moreover, manual evaluation struggles to accurately quantify complex metrics like image realism and text-image matching, limiting precise model iteration guidance.
To address these challenges, EvalScope offers a comprehensive solution from automated evaluation to intelligent analysis. Its core advantages include:
-
Automated Evaluation Capability: Supports batch inference and metric calculation for mainstream text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion and Flux, using models like MPS and HPSv2.1Score to assess image realism and text-image alignment. This replaces traditional manual annotation with scripted processes. For more supported metrics and datasets, refer to the documentation: EvalScope Documentation.
-
Intelligent Reporting and Visualization: Utilizes large models to automatically generate multi-dimensional analysis reports, combined with interactive visualization tools like radar and bar charts, to intuitively display model performance differences across scenarios, aiding developers in quickly identifying model bottlenecks.
This document uses FLUX.1-dev and HiDream-I1-Dev models as evaluation subjects on the EvalMuse dataset, providing developers with a complete practice guide from environment setup to result interpretation, leveraging EvalScope's intelligent reporting and visualization features.
Installing Dependencies
First, install the EvalScope model evaluation framework:
pip install 'evalscope[aigc,app]' -U
To use the latest text-to-image models, including HiDream-I1-Dev, install the latest diffusers library:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
Running Evaluation Tasks
Next, we will comprehensively test text-to-image models using the EvalMuse benchmark. EvalMuse focuses on "text-image" alignment capabilities with nearly 200 diverse prompts covering semantic tags like objects, colors, quantities, and actions, enabling multi-dimensional performance analysis through structured annotation. You can view prompt samples on the ModelScope community dataset page: EvalMuse Dataset Samples.
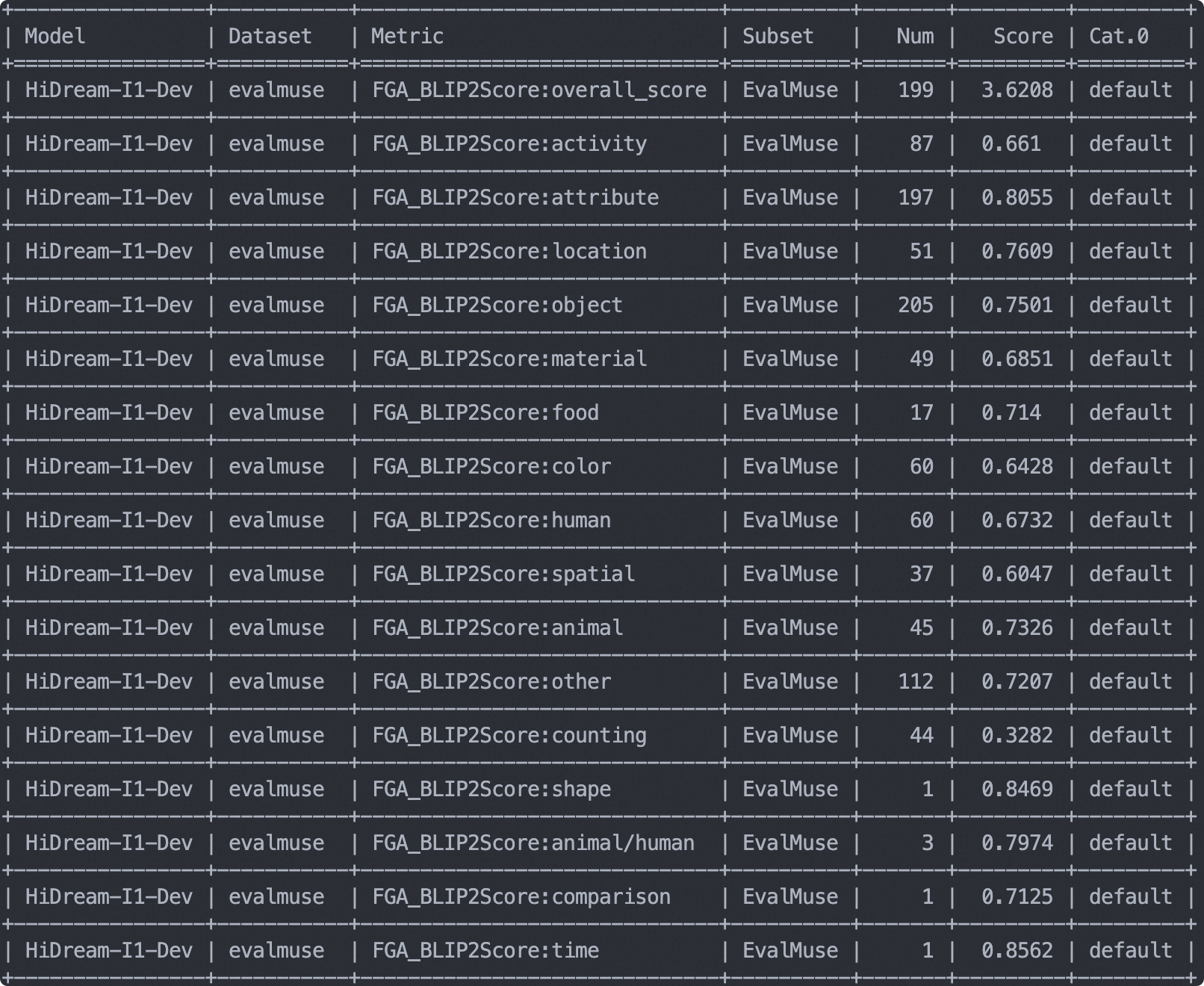
This evaluation uses FGA-BLIP2 as an automated scoring model, replacing traditional manual annotation to significantly improve efficiency. The scoring system consists of two parts: an overall score (0-5) for evaluating the comprehensive quality and text matching of generated images, and subcategory scores (0-1) for specific semantic tags like objects, colors, and quantities. This method avoids subjective bias and ensures reproducible results, especially suitable for large-scale model comparison tests.
Run the following code to start the full evaluation process. The system will automatically download the text-to-image model, evaluation dataset, and scoring model (the first run may take a long time to download, please be patient), and complete inference with approximately 60GB of VRAM support.
Note: After the evaluation, the Qwen3-235B-A22B large model API will be called to generate an intelligent report. Please obtain the MODELSCOPE_SDK_TOKEN from the ModelScope community and configure it in the environment variable in advance. Get it here: Token Page.
from evalscope.constants import ModelTask
from evalscope import TaskConfig, run_task
from modelscope import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
# HiDream model requires llama-3.1-8b-instruct model as Encoder
tokenizer_4 = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("LLM-Research/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct")
text_encoder_4 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"LLM-Research/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
output_hidden_states=True,
output_attentions=True,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
# Configure evaluation parameters
task_cfg = TaskConfig(
model='HiDream-ai/HiDream-I1-Dev', # Specify model id on modelscope
model_task=ModelTask.IMAGE_GENERATION, # Must be IMAGE_GENERATION
# Configure model parameters, refer to the corresponding Pipeline for supported parameters
model_args={
'pipeline_cls': 'HiDreamImagePipeline', # Specify using HiDreamImagePipeline
'torch_dtype': 'torch.bfloat16', # Use bfloat16 precision
'tokenizer_4': tokenizer_4, # Specify tokenizer
'text_encoder_4': text_encoder_4, # Specify text encoder
},
# Configure evaluation dataset
datasets=[
'evalmuse',
],
# Configure model generation parameters, refer to the corresponding Pipeline for supported parameters
generation_config={
'height': 1024, # Image height
'width': 1024, # Image width
'num_inference_steps': 28, # For HiDream-Dev, recommended steps are 28
'guidance_scale': 0.0, # For HiDream-Dev, recommended is 0.0
},
# Whether to generate an analysis report
analysis_report=True,
)
# Run evaluation task
run_task(task_cfg=task_cfg)
The evaluation output shows the model's scores across different dimensions:
To further test the FLUX.1-dev model, run the following code:
task_cfg = TaskConfig(
model='black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev', # model id
model_task=ModelTask.IMAGE_GENERATION, # must be IMAGE_GENERATION
model_args={
'pipeline_cls': 'FluxPipeline',
'torch_dtype': 'torch.float16',
},
datasets=[
'evalmuse',
],
generation_config={
'height': 1024,
'width': 1024,
'num_inference_steps': 50,
'guidance_scale': 3.5
},
analysis_report=True,
)
run_task(task_cfg=task_cfg)
Additionally, the EvalScope framework supports specifying prompts and image paths for custom model evaluation, not limited to local text-to-image inference. For specific usage, refer here: EvalScope Documentation.
Visualization of Evaluation Results
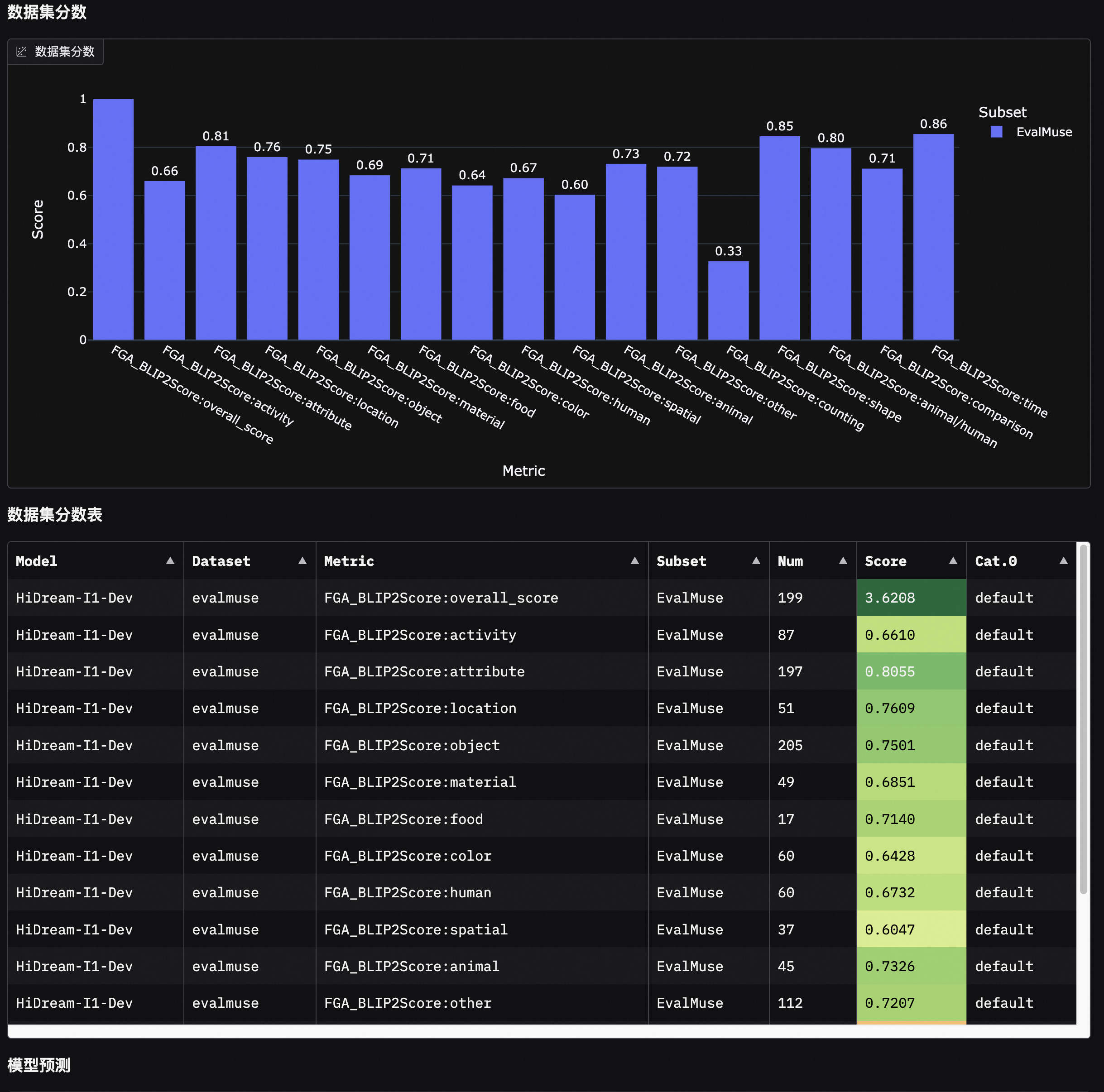
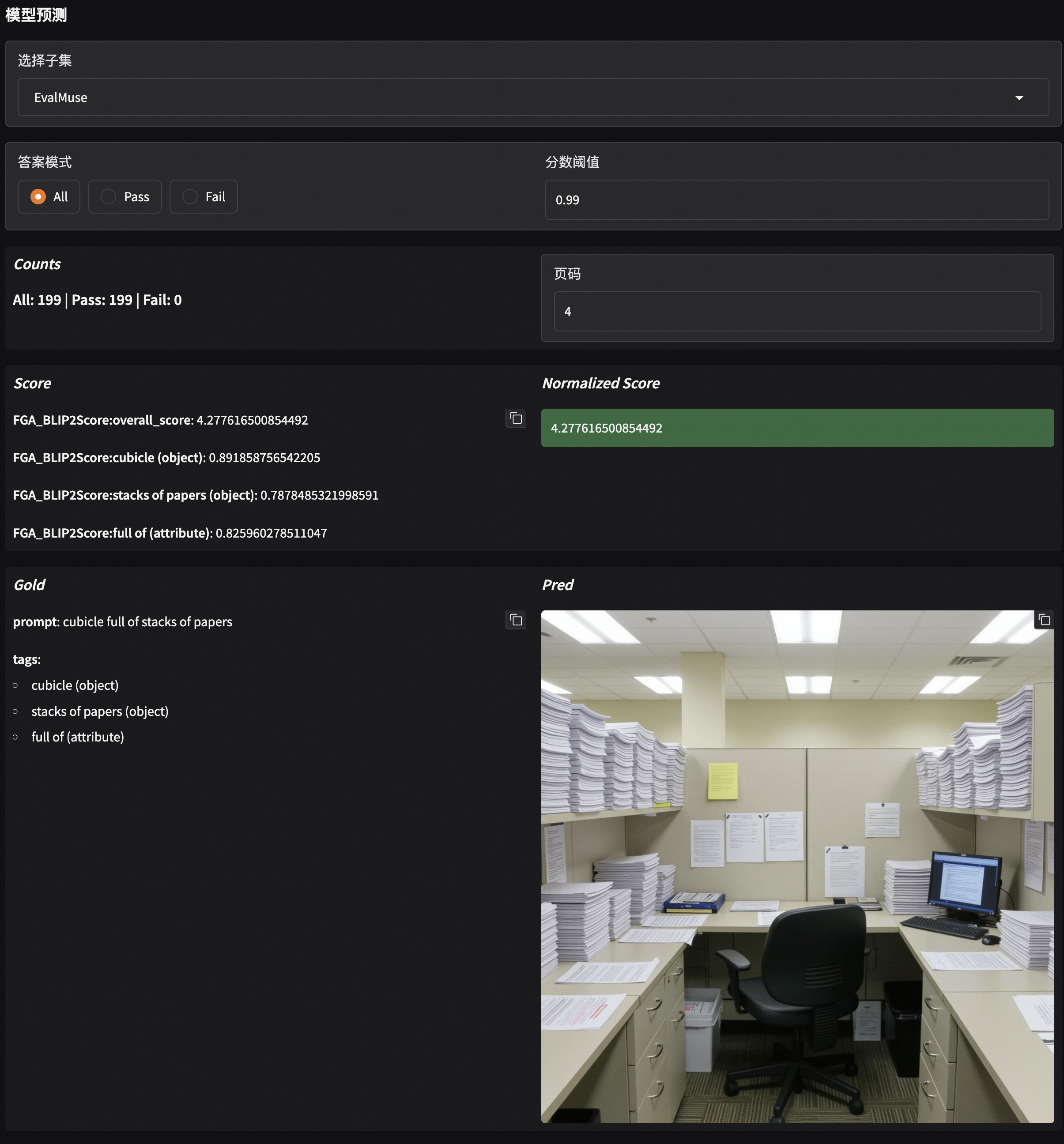
Run the following command to launch the visualization interface, intuitively displaying model evaluation effects and analyzing model outputs:
evalscope app
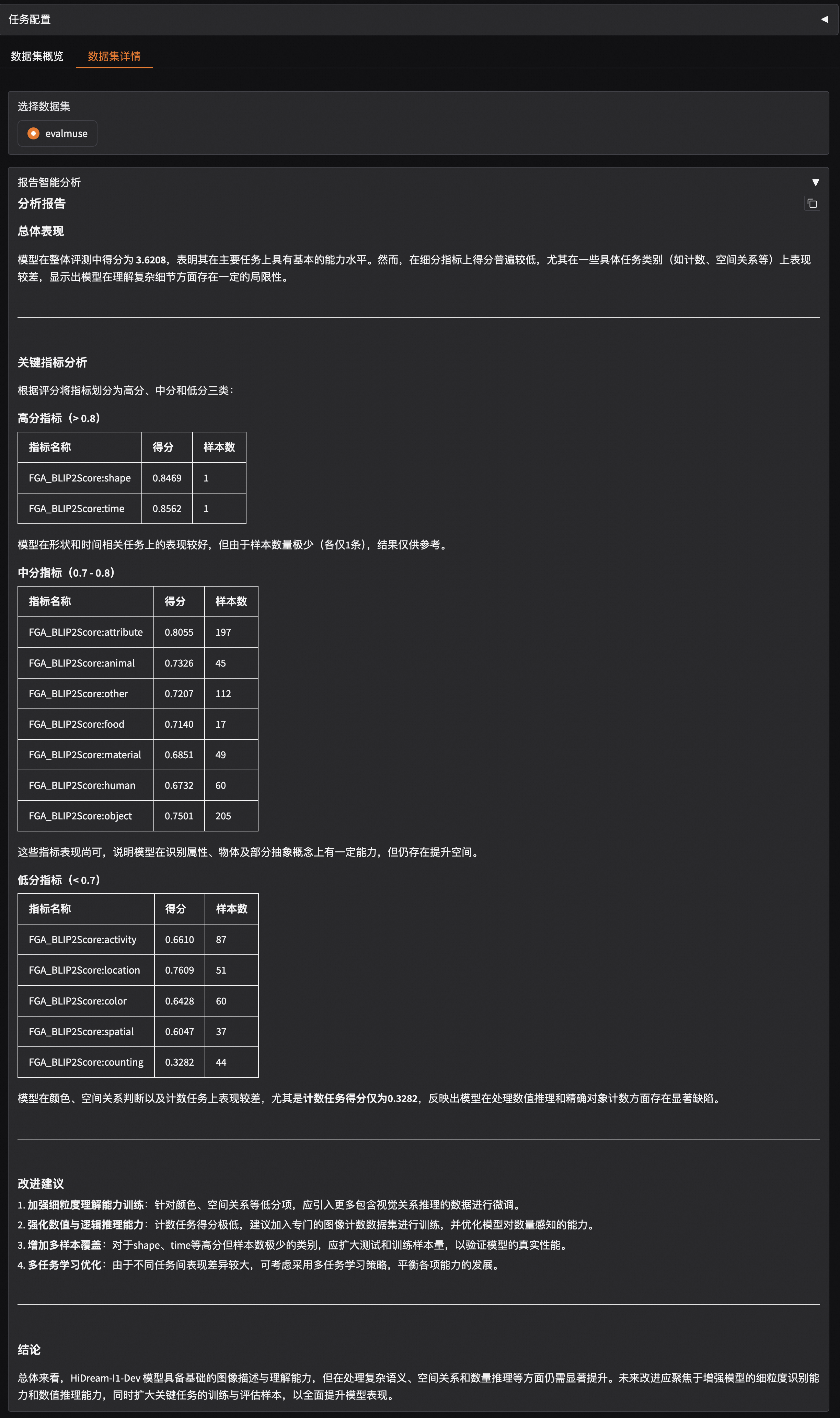
The evaluation results include intelligent analysis reports, model score distribution, and generated image cases. The analysis report shows that the HiDream-I1-Dev model performs well in image description and understanding but needs improvement in handling complex semantics, spatial relationships, and quantity reasoning.
We can also compare the results with the official EvalMuse test results. HiDream-I1-Dev ranks third in this framework, indicating good overall performance. Although the model data is not included in the table, this external validation shows that our evaluation framework effectively reflects the model's true performance level, comparable to the official EvalMuse benchmark test.
Conclusion
The automated evaluation provided by the EvalScope framework objectively achieves full-process automation from batch inference to multi-dimensional analysis. Combined with intelligent report analysis and result visualization, it significantly enhances the efficiency and objectivity of text-to-image model performance evaluation. We hope these efforts help address the issues of relying on extensive human resources for sample selection and subjective scoring in traditional manual evaluation, reducing evaluation cycles and costs, and avoiding subjective bias that affects evaluation results. On this basis, we will further improve the capabilities of the EvalScope evaluation framework and introduce evaluation standards that cover more aspects, facilitating developers to conduct more comprehensive and targeted evaluations of model performance in different scenarios.
References
-
Zhang, S. et al. Learning Multi-dimensional Human Preference for Text-to-Image Generation. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2405.14705(2024).
-
Wu, X. et al. Human Preference Score v2: A Solid Benchmark for Evaluating Human Preferences of Text-to-Image Synthesis. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.09341(2023).
-
Chang, L.-W. et al. FLUX: Fast Software-based Communication Overlap On GPUs Through Kernel Fusion. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.06858(2024).
-
Cai, Q. et al. HiDream-I1: A High-Efficient Image Generative Foundation Model with Sparse Diffusion Transformer. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2505.22705(2025).
-
Han, S. et al. EvalMuse-40K: A Reliable and Fine-Grained Benchmark with Comprehensive Human Annotations for Text-to-Image Generation Model Evaluation. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2412.18150(2024).